

Malnutrition in India
Malnutrition among women and children is extremely high in India. Every second woman in the country is anemic, every third child is stunted and malnourished and every fifth child is wasted, according to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) 2015-16.
Furthermore, recent statistics indicate a rise in anemia levels among women and children (NFHS-5). Iron deficiency anemia is the biggest cause of disability for the past 10 years and contributed to 20 percent of direct and 50 percent of associated maternal deaths in India. Its economic burden is equivalent to about 4 percent of GDP. Apart from iron, deficiency in micronutrients like vitamin B12, vitamin A, folate, and zinc also contribute to rising anemia levels.
Micronutrient deficiency or micronutrient malnutrition, also known as “hidden hunger,” is a serious health risk.
Dietary diversification, micronutrient supplementation, and staple food fortification are globally recognized three options to combat micronutrient deficiencies, Of these, “Staple Food Fortification´ is considered the most cost-effective complementary strategy with demonstrated results, worldwide, across all population groups.
Why Fortify Rice?
Since rice is one of India’s staple diets consumed by about two-thirds of the population and per capita, rice consumption is 6.8 kg per month. As a result, fortifying rice with micronutrients is an option for supplementing the poor’s diet. Rice fortification with micronutrients is thus an ideal vehicle for bridging dietary nutrient gaps and improving health outcomes, particularly for vulnerable populations.
Considering the serious issue of anemia due to malnutrition, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced mandatory rice fortification in all social safety net schemes by 2024.
As per NITI Aayog, with this announcement of universal rice fortification by 2024, about 100 crore people will be covered, including about 20 crore women of reproductive age.

Fortified Rice Kernels
What is Rice Fortification?
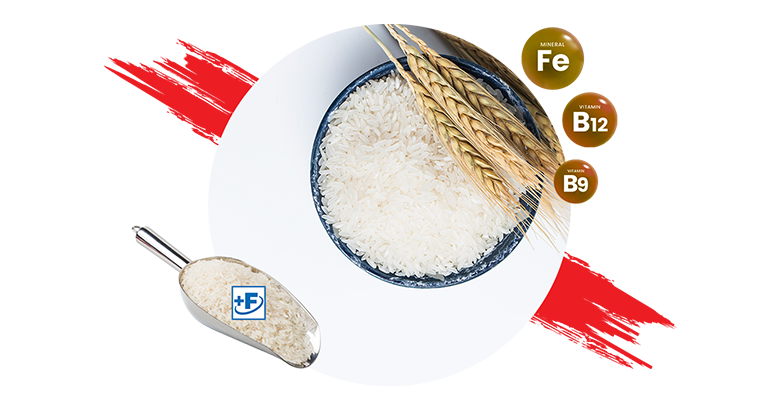
Rice fortification, is a process of adding micronutrients like iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12. Additionally, rice can be fortified with micronutrients such as zinc, Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin B2, Vitamin B3, and Vitamin B6. Thus, rice fortification helps to improve the nutritional quality; provides immense public health benefits by way of substantial reduction in anemia levels; and can thus serve as an effective, preventive, and cost-efficient complementary strategy to address the widespread micronutrient malnutrition problem within a short period.
The fortification of rice can help a large portion of the world’s population get the necessary vitamins, minerals, and micronutrients to improve their health and fight malnutrition.
Micronutrients are mixed with regular rice in various ways, such as extrusion, coating, and dusting.
The extrusion process uses a machine to produce fortified rice kernels (FRKs). Rice flour is pulverized and combined with a vitamin and mineral premix. An extruder machine is used to make fortified rice kernels from this mixture. Fortified Rice Kernels are similar in size, shape, and color to milled rice, but they contain additional vitamins and minerals. Fortified rice kernels (FRKs) contain mandatory micronutrients (Iron, Folic Acid, and Vitamin B12), or optional (Zinc, Vitamin A, Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, and Pyridoxine) as per levels given by Food Safety and Standards (Fortification of Foods) Regulations, 2018. FRK produced through the extrusion process, retain their micronutrient content after being washed and boiled in water
Fortified rice is made by mixing fortified rice kernels with normal rice. This is the most commonly used method of fortifying rice. In this process, fortified rice is milled rice (of any variety), which is blended with extruded rice-shaped kernels, fortified with essential vitamins and minerals, in the ratio of 1:100.
Standards for Rice fortification as per FSSAI recommendations:
1 kg of fortified rice will contain iron (28 mg-42.5 mg), folic acid (75-125 mg), and Vitamin B-12 (0.75-1.25 mg). Rice may also be fortified with zinc (10 mg-15 mg), vitamin A (500-750 mg), vitamin B-1 (1-1.5 mg), vitamin B-2 (1.25-1.75 mg), vitamin B-3 (12.5-20 mg) and vitamin B-6 (1.5-2.5 mg) per kg.
In what ways do we distinguish fortified rice from regular rice
Fortified rice will be packed in bags with the logo (‘+F’) and the line “Fortified with Iron, Folic Acid, and Vitamin B12”.
Hexagon Nutrition at the forefront of rice fortification:
A leader in global health innovation, it is at the forefront of finding and implementing effective approaches to boost and enhance rice fortification across the world. As a preferred partner for many renowned fortified rice brands, Hexagon Nutrition caters to the micronutrient premix requirements to produce FRK. With a goal to alleviate malnutrition through food fortification, Hexagon Nutrition manufactures, markets & supplies scientifically formulated premixes to governments, multinational food manufacturers, and international NGOs globally. Visit https://87f.1e3.myftpupload.com/frk to know more about the rice fortification process and services.
Sources:
https://www.drishtiias.com/daily-updates/daily-news-analysis/rice-fortification
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/what-is-fortified-rice-how-is-it-prepared-7860432/
https://www.niti.gov.in/rice-fortification-effective-way-combat-anemia



